“Combinatorial testing can detect hard-to-find software faults more efficiently than manual test case selection methods.”
Developers of large data-intensive software often notice an interesting—though not surprising—phenomenon: When usage of an application jumps dramatically, components that have operated for months without trouble suddenly develop previously undetected errors. For example, newly added customers may have account records with an oddball combination of values that have not been seen before. Some of these rare combinations trigger faults that have escaped previous testing and extensive use. Alternatively, the application may have been installed on a different OS-hardware-DBMS-networking platform. Combinatorial testing can help detect problems like this early in the testing life cycle. The key insight underlying t-way combinatorial testing is that not every parameter contributes to every fault and many faults are caused by interactions between a relatively small number of parameters.

PAIRWISE TESTING
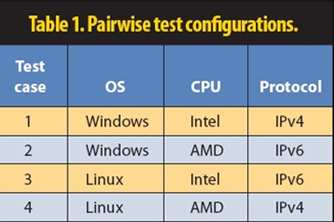
Suppose we want to demonstrate that a new software application works correctly on PCs that use the Windows or Linux operating systems, Intel or AMD processors, and the IPv4 or IPv6 protocols. This is a total of 2 × 2 × 2 = 8 possibilities but, as Table 1 shows, only four tests are required to test every component interacting with every other component at least once. In this most basic combinatorial method, known as pairwise testing, at least one of the four tests covers all possible pairs (t = 2) of values among the three parameters.
Note that while the set of four test cases tests for all pairs of possible values—for example, OS = Linux and protocol = IPv4—several combinations of three specific values are not tested—for example, OS = Windows, CPU = Intel, and protocol = IPv6.
Even though pairwise testing is not exhaustive, it is useful because it can check for simple, potentially problematic interactions with relatively few tests. The reduction in test set size from eight to four shown in Table 1 is not that impressive, but consider a larger example: a manufacturing automation system that has 20 controls, each with 10 possible settings—a total of 1020 combinations, which is far more than a software tester would be able to test in a lifetime. Surprisingly, we can check all pairs of these values with only 180 tests if they are carefully constructed.
Figure 1 shows the results of a 10-project empirical study conducted recently by Justin Hunter that compared the effectiveness of pairwise testing with manual test case selection methods.

The projects were conducted at six companies and tested commercial applications in development; in each project, two small teams of testers were asked to test the same application at the same time using different methods. One group of testers selected tests manually; they relied on “business as usual” methods such as developing tests based on functional and technical requirements and potential use cases mapped out on whiteboards. The other group used a combinatorial testing tool to identify pairwise tests. Test execution productivity was significantly higher in all of the projects for the testers using combinatorial methods, with test execution productivity more than doubling on average and more than tripling in three projects. The groups using pairwise testing also achieved the same or higher quality in all 10 projects; all of the defects identified by the teams using manual test case selection methods were identified by the teams using combinatorial methods. In five projects, the combinatorial teams found additional defects that had not been identified by the teams using manual methods.
These proof-of-concept projects successfully demonstrated to the teams involved that manual methods of test case selection were not nearly as effective as pairwise combinatorial methods for finding the largest number of defects in the least amount of time.
TESTING HIGHER-DEGREE INTERACTIONS
Other empirical investigations have concluded that from 50 to 97 percent of software faults could be identified by pairwise combinatorial testing. However, what about the remaining faults? How many failures could be triggered only by an unusual interaction involving more than two parameters?
In a 1999 study of faults arising from rare conditions, the National Institute of Standards and Technology reviewed 15 years of medical device recall data to determine what types of testing could detect the reported faults (D.R. Wallace and D.R. Kuhn, “Failure Modes in Medical Device Software: An Analysis of 15 Years of Recall Data,” Int’l J. Reliability, Quality, and Safety Eng., Dec. 2001, pp. 351-371). The study found one case in which an error involved a four-way interaction among parameter values: demand dose = administered, days elapsed = 31, pump time = unchanged, and battery status = charged.
Pairwise combinatorial testing is unlikely to detect faults like this because it only guarantees that all pairs of parameter values will be tested. A particular four-way combination of values is statistically unlikely to occur in a test set that only ensures two-way combination coverage; to ensure thorough testing of complex applications, it is necessary to generate test suites for four-way or higher-degree interactions.
Investigations of other applications found similar distributions of fault-triggering conditions. Many faults were caused by a single parameter, a smaller proportion resulted from an interaction between two parameter values, and progressively fewer were triggered by three-, four-, five,- and six-way interactions.
Figure 2 summarizes these results. Thus far, a fault triggered by a seven-way interaction has not appeared.

With the Web server application, for example, roughly 40 percent of the failures were caused by a single value, such as a file name exceeding a certain length; another 30 percent were triggered by the interaction of two parameters; and a cumulative total of almost 90 percent were triggered by three or fewer parameters.
While not conclusive, these results suggest that combinatorial methods can achieve a high level of thoroughness in software testing.
The key ingredient for this kind of testing is a covering array, a mathematical object that covers all t-way combinations of parameter values at least once. For the pairwise testing example in Table 1, t = 2, and it is relatively easy to generate tests that cover all pairs of parameter values. Generating covering arrays for complex interactions is much harder, but new algorithms make it possible to generate covering arrays orders of magnitude faster than previous algorithms, making up to six-way covering arrays tractable for many applications.
Figure 3 shows a covering array for all three-way interactions of 10 binary parameters in only 13 tests. Note that any three columns, selected in any order, contain all eight possible values of three parameters: 000,001,010,011, 100,101,110,111. Three-way interaction testing detected roughly 90 percent of bugs in all four of the empirical studies in Figure 2, but exhaustive testing of all possible combinations in Figure 3 would require 210 = 1,024 tests.

What are the pragmatic implications of being able to achieve 100 percent three-way coverage in 13 test cases on real-world software testing projects? Assuming that there are 10 defects in this hypothetical application and that 9 are identified through the 13 tests indicated, testing these 13 cases would find 71 times more
defects per test case [(9/13)/(10/1,024)] than testing exhaustively and uncovering all 10.
While the most basic form of combinatorial testing— pairwise—is well established, and adoption by software testing practitioners continues to increase, industry usage of these methods remains patchy at best. However, the additional training required is well worth the effort. Teams seeking to maximize testing thoroughness given tight time or resource constraints, and which currently rely on manual test case selection methods, should consider pairwise testing. When more time is available or more thorough testing is required, t-way testing for t > 2 is better. Practitioners who require very high quality software will find that covering arrays for higher-strength combinations can detect many hard to-find faults, and variability among detection rates appears to decrease as t increases.
Sophisticated new combinatorial testing algorithms packaged in user-friendly tools are now available to enable thorough testing with a manageable number of test cases and at lower cost, and make it practical for testers to develop empirical results on applications of this promising test method.
Article By
D. Richard Kuhn, Computer Scientist, NIST
Raghu Kacker, Mathematical Statistician, NIST
Yu Lei, Associate Professor, University of Texas at Arlington
Justin Hunter, CEO, Hexawise
Download here

 Rick Kuhn
Rick Kuhn Raghu Kacker
Raghu Kacker Justin Hunter
Justin Hunter















