Mobile testers need to take a different approach when it comes to Test Automation.
Anyone who is involved in software testing and software Test Automation should know the Test Automation pyramid introduced by Mike Cohn (www.mountaingoatsoftware.com/).
This article contains excerpts from my book Hands-On Mobile App Testing published with Pearson Education.
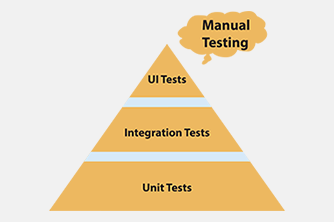
As you can see in the following image, the typical pyramid consists of three layers. At the bottom, there is the automated unit-testing layer, in the middle the automated integration testing layer and at the top there is the automated end-to-end testing layer (including the user interface tests). Each layer has a different size, indicating the number of tests that should be written within each stage. Manual testing is not part of the test pyramid, hence it is shown as a cloud for additional testing work.
But this pyramid is not applicable to mobile apps and mobile test automation. Mobile testing requires a totally different set of testing activities like movement, sensors, different devices and networks compared to other software like desktop or web applications. Lots of manual testing is required to be sure that a mobile app is working as expected in the different usage scenarios.
Mobile Test Automation tools are currently not as mature as their counterparts for web and desktop applications, which leads to a flipped Test Automation pyramid. As the tools become increasingly mature, this pyramid is likely to flip back again because the default Test Automation pyramid is based on a more stable foundation (see the pyramid image below).
The default pyramid therefore can’t be used as an indicator for Test Automation and Manual Testing in the mobile world. The flipped testing pyramid looks like this: In this version of the pyramid, the automated unit testing layer is the smallest one. This is the case because not
The flipped testing pyramid looks like this:
In this version of the pyramid, the automated unit testing layer is the smallest one. This is the case because not every unit or method of mobile apps can be tested in an isolated manner. In some cases, different APIs, layers or systems may need to be faked or mocked in order to get the small unit to work. This is also the case for every other software application, but in some cases mocking or faking other systems for mobile apps is much more complex. This is not efficient from a technical or economic point of view. However, it’s no excuse for not writing mobile unit tests at all. The main logic of an app can/must be tested at the unit level.
The next stage is the end-to-end Test Automation layer. Within this layer, the whole app is tested from a user perspective. It will be tested to make sure the whole system is working, from the app’s user interface through to the backend system via a wireless network, including integration testing with different libraries or APIs. The integration testing layer is therefore part of the end-to-end layer.
The biggest change in this pyramid is that manual testing is part of it. Mobile testing requires lots of Manual Testing, and this can’t be replaced by Test Automation or any other tools yet.
Nevertheless, mobile Test Automation is a really important topic and every mobile tester should be able to write automated regression tests that provide fast feedback about the current quality state of an app. Furthermore, Test Automation helps the team build a reliable and robust mobile app that makes the customers happy.
Mobile Test Pyramid
The flipped testing pyramid has no stable foundation and mobile testing requires lots of Manual Testing, which is why I created my own mobile test pyramid consisting of four layers including Manual and Automated steps. The biggest layer of the pyramid is Manual Testing and forms the strong foundation for every mobile app project, followed by end-to-end testing, beta testing and a top layer comprising unit testing. The grey parts of the pyramid indicate the automated steps and the white parts are the Manual Testing steps. The beta-testing layer is new to the pyramid but essential to every mobile app project. Keeping the high expectations of the mobile users in mind requires this layer to be part of every mobile project to get early feedback from your mobile customers. You can either use a crowd testing approach for your beta testing or you can ask your colleagues to beta test early versions of your app to provide important feedback.
Note: The End-2-End and Unit tests layers can also be swapped as well as the beta and End-2-End layer. The amount of End-2-End tests and Unit tests can differ from project to project and from app to app.
I used this mobile test pyramid in several projects and it helped me set up a reliable, effective and valuable testing process.
If you want to read more about mobile testing, please have a look at my book Hands-On Mobile App Testing which is available as a printed copy as well as an eBook. More details under: http://www.handsonmobileapptesting.com/ or in any other online or offline bookstore.